The Physical Workspace: Distance Measurements
The Physical Workspace provides the dimension of distance to Ethernet and wireless devices. This distance parameter is one of the factors that determine if a device is able to connect or not connect to another device.
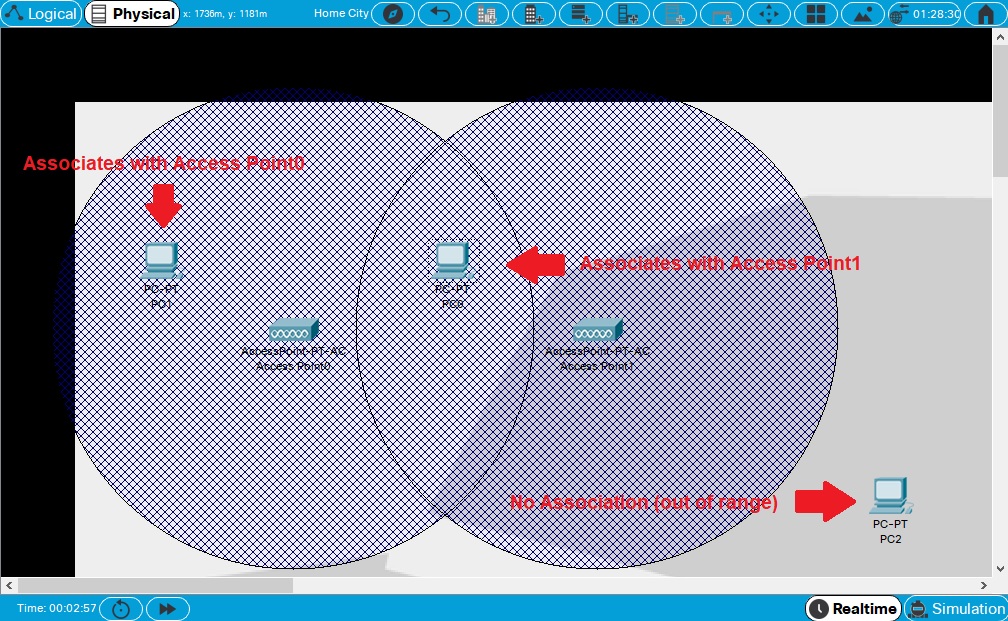
Access points can establish connections with wireless end devices that are within a certain distance range. This range is indicated by a gray mesh area surrounding the access point. Note that this mesh area appears as a circle or an oval depending on the dimensions of the background image used. If the background source image is square, the mesh is circular. If the background image is a rectangle, the mesh is oval, scaled by the width and height of the source image.
In this example, three wireless-enabled PCs and two access points are created. They have all been moved from the default wiring closet and placed directly onto the "streets" of the city (for demonstration purposes). Note the following:

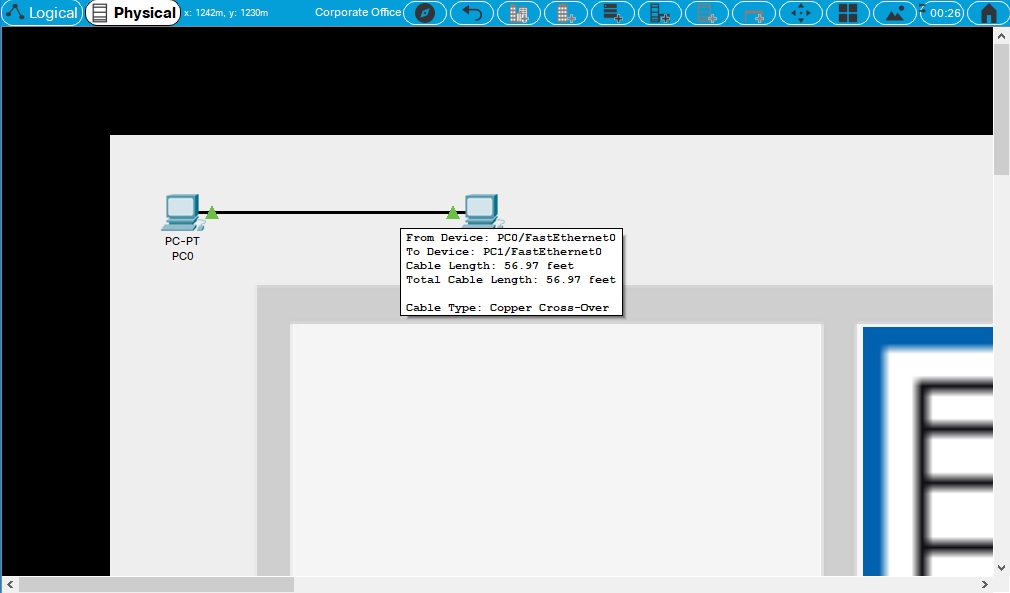
Ethernet connectivity is determined by a cable length of 100 meters. There is no partial connectivity for Ethernet, it is either within (has connectivity) the length of 100 meters or outside (no connectivity) of it. By pointing at a cable in physical mode, a pop-up box will appear showing the device interfaces connected to this cable and the segment and total length.
Packet Tracer now also has the ability to bend, group and color code cables. This feature is covered in the Cable Manipulation section.